-
Hip Pain
Hip pain, one of the common complaints, may not always be felt precisely over the hip joint rather in and around the hip joint. The cause for pain is multifactorial and the exact position of your hip pain suggests the probable cause or underlying condition causing it.
-
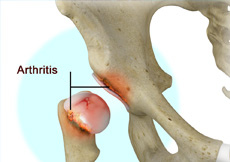
Arthritis of the Hip
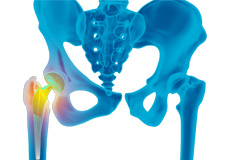
When the cartilage is damaged, the two bones rub against each other causing pain, swelling and stiffness of the joint. This condition is called arthritis. Arthritis is a progressive disorder, and is the most common cause of joint pain.
-
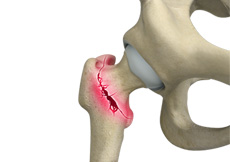
Hip Fracture
The hip joint is a "ball and socket" joint. The "ball" is the head of the femur or thighbone, and the "socket" is the cup-shaped acetabulum. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint.
-
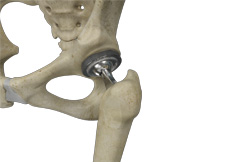
Painful Total Hip Replacement
A hip replacement is a surgical procedure where an injured or damaged hip joint is replaced with an artificial hip joint known as a prosthesis. Reoperation may be necessary to resolve pain in a hip replacement due to a damaged, misaligned or worn-out part of the artificial hip joint, or repair of a muscle.
-
Avascular Necrosis of the Hip
Avascular necrosis, also called osteonecrosis, is a condition in which bone death occurs because of inadequate blood supply to it. Lack of blood flow may occur when there is a fracture in the bone or a joint dislocation that may damage nearby blood vessels. Hip joint is most commonly affected; however, the knee and shoulder may also be involved.
-
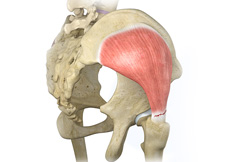
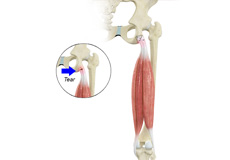
Hip Abductor Tears
Hip abductors are a major group of muscles found in the buttocks. It includes the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fascia lata muscles.
-
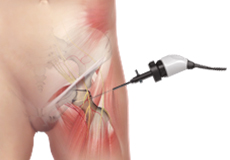
Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is a surgical procedure in which an arthroscope is inserted into your hip joint to check for any damage and repair it simultaneously.
-
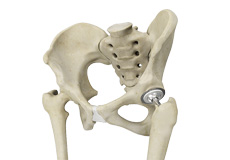
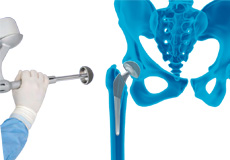
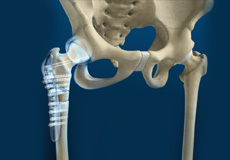
Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components. The main indication for total hip replacement is arthritis.
-
Posterior Total Hip Replacement
Posterior hip replacement is a minimally invasive hip surgery performed to replace the hip joint. It is also referred to as muscle sparing surgery because no muscles are cut to access the hip joint, enabling a quicker return to normal activity.
-
Anterior Total Hip Replacement
Direct anterior hip replacement is a minimally invasive hip surgery to replace the hip joint without cutting through any muscles or tendons as against traditional hip replacement that involves cutting major muscles to access the hip joint.
-
Minimally Invasive Total Hip Replacement
Minimally invasive total hip replacement is a surgical procedure performed through one or two small incisions rather than the single long incision of 10–12-inches as in the traditional approach.
-
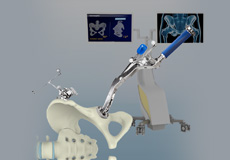
Robotic Assisted Total Hip Replacement
Robotic total hip replacement is a minimally invasive procedure where your surgeon is assisted by a robotic system to perform a total hip replacement surgery.
-
Computer-Navigated Total Hip Replacement
For a successful total hip replacement, accurate positioning of the implants is crucial to accomplish a good clinical outcome. Computer-navigated total hip replacement is an advanced technology developed to provide more accurate positioning of an implant. Hip replacement through computer navigation provides information and guidance to the surgeon for precise positioning of implants.
-
Outpatient Total Hip Replacement
Hip replacement surgery is one of the most common orthopedic surgeries performed. It involves the replacement of the damaged hip bone (ball shaped upper end of the femur) with a ceramic ball attached to a metal stem that is fixed into the femur and placing a new cup with a special liner in the pelvis.
-
Revision Total Hip Replacement
During total hip replacement, the damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components. At times, hip replacement implants can wear out for various reasons and may need to be replaced with the help of a surgical procedure known as revision hip replacement surgery.
-
Hip Fracture Surgery
Surgical correction of a hip fracture is known as hip fracture surgery. Hip fractures involve a break that occurs near the hip in the upper part of the femur or thigh bone. The thigh bone has two bony processes on the upper part - the greater and lesser trochanters. The lesser trochanter projects from the base of the femoral neck on the back of the thigh bone.
-
Proximal Hamstring Repair
The hamstrings are a group of three thigh muscles that extend from the pelvis to the knee joint. They include the:
- Bicep femoris
- Semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
These muscles help in extending your leg and bending your knee. Therefore, any damage to the hamstring muscle group affects both hip and knee movements.
-
Non-Surgical Hip Treatments
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint that connects the thigh bone to the pelvic bone. As a major weight-bearing joint with a wide range of motion, the hip is susceptible to various kinds of injuries. Hip problems may arise with overuse, acute trauma, degenerative diseases such as arthritis, and sports injuries.
-
O. David Taunton, Jr., M.D.Hip & Knee
-
Nathan B. Haile, M.D.Hip & Knee
-
Katherine C. Bartush, M.D.Sports Medicine
Foot & Ankle